| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 2004 ---> Data Processing: High Resolution Data Processing |
The Mathematic Model and
Application of Satellite Phototopography
Yang Ming Hui Ren Wei
Chun
Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping
No16 Bei Tai Ping Road ,Haidian district, Beijing, 100039, China
Tel: (86)-10-68222464, Fax: (86)-10-68218654
Email: minghui@casm.ac.cn
Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping
No16 Bei Tai Ping Road ,Haidian district, Beijing, 100039, China
Tel: (86)-10-68222464, Fax: (86)-10-68218654
Email: minghui@casm.ac.cn
1 .The development of Satellite Phototopography
In twenty first century ,The Topography are developing to a new stage of Satellite Phototopography and Aerophototopography .
The Global positioning system are used for positioning of the sensor or antenna position on orbit with required accuracy of topographic control measurement, and the Inertial Measurement unit and stellar observation are used for determination of the direction of earth observation, So that adopting Satellite Phototopography, The topographic surveying and mapping including stereomapping , DEM measurement , orthophotomapping could be conducted with a few control points measurement on the field.
SPOT-5 are an Typical phototopographic satellite: HRG collected image with 2.5 meter resolution can be used to orthophoto mapping and detail mapping in scale 1:50000 and 25000; Through forward and backward vision, HRS can collect the topographic data and DEM data for stereomapping in range 600 km_by_ 120 km . Besides of spatial resolution increased to 0.7 meter, Planning SPOT Pleiades-HR have the capability to collect stereo and tri-stereo imagery for large image coverage through lateral vision and forward/backward vision, as well the capability for surveying and mapping along a river, border and coast line.
The Satellite Phototopography is developing which has the new characteristic as following : For Satellite Phototopography, The instantaneous satellite position on orbit will be a station from which the forward intersection are carried on, So, the position of station should be computed by using satellite geodesy method and with the accuracy topographic control survey required. With high accuracy time and stable velocity, for a temporal period, Satellite move along the orbit a step correspondence to spatial resolution.
Either lateral vision or forward/backward vision along orbit the visual direction of sensor are determined by attitude angle. Therefore the grouped stellar observation / IMU system are important part of satellite phototopographic system.
Along with the development of spatial and temporal measurement technology, satellite phototopographic survey could be conducted with only a few control measurements on the ground.
2 .The mathematic model of Satellite Phototopography
2.1 Satellite topographic control measurement
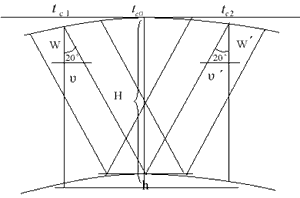
Figure 1.1 HRS forward intersection The data collection and processing of satellite phototopography are conducted in orbital reference or instantaneous orbital reference. At first the satellite positioning are computed by using satellite geodesy method and with higher accuracy that topographic control survey requires. From P(t) and V(t) in SPOT documentation the instantaneous position and velocity could be interpolated with formula following:
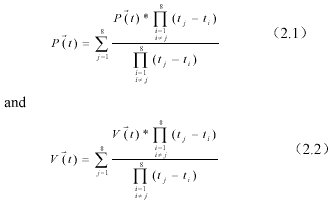
According to (2.1).(2.2), The transformation can be derived for transforming WGS-84 geocentric reference to orbital reference.
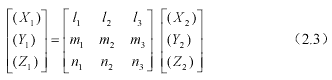
Or vice versa from orbital reference toWGS-84 geocentric reference
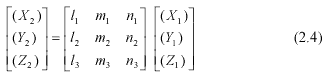
2.2Ortho rectification with SPOT-5 image,
In the satellite phototopogpaphy, the satellite position on the orbit is an instantaneous station, from which the forward intersection are carried on either for HRS or HRG image:
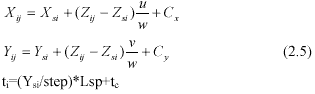
In formula (2.5)
tc are the time for scene centre ti are the time to collect the image line data.
Constant Cx , Cy are systematic errors correction which are caused mainly by absolute attitude errors.
Formula (2.6) can be used to estimate the accuracy of SPOT-5 orthorectification:
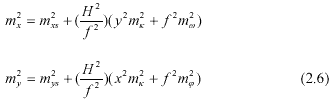
2.3Stereoscopic measurement with SPOT-5 HRS With forward/backward images of SPOT-5 HRS, stereoscopic measurement could be conducted. So that relative and absolute orientation will be computed in a rotated orbital reference. Relative orientation:
The coordinate transformation in image space :
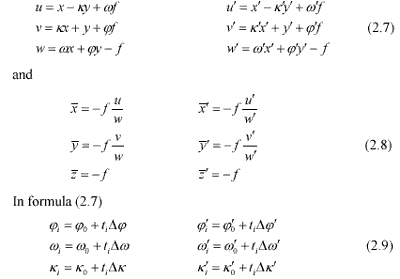
Then the “ relative orientation ” can be computed with x parallax condition (2.10) which enters the attitude angle correction, and makes conjugate visual vector intersection:
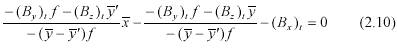
Absolute orientation:
From figure (2.1), An elevation condition can be derived as formula (2.11) which enters mainly the absolute roll angle correction and makes platform horizontal.
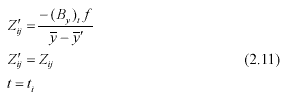
Formula (2.10) and (2.11) are differentiated for variation k w j , , and k w j ¢ ¢ ¢ , ,, and with ground control point, a group of errors equation are constituted. From iterative normal equations solution, the moving base forward intersection model can be established. The accuracy of HRS stereoscopic measurement can be estimated as:
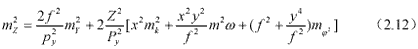
From formula (2.6) and (2.12), It is obvious either elevation or coordinate accuracy are very depends on attitude angles determination.
3. The presentation for part of test works
For verifying the mathematic model (2.5)(2.10 )and (2.11 )correct, HRS forward/ backward images and HRG image in western part of China are provided by Beijing SPOT IMAGE .With DEM data digitized from topographic map in scale 1: 50000 and control points as well check points pick up on map .New SPOT image software developing are cooperated by Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping and Beijing Si-Wei New Century Information Technology Ltd .

Image 1: orthorectification with HRS image

Image 2 : Orthorectification with HRG image
Image 1 and image 2 are the test results calculated with the mathematic model and software developed by Beijing Si-Wei New Century company.
Image 1 covers hilly area, after orthorectification with 11 check points the mean square errors are calculated as mx =11.7m, my=8.0m, ms=14.2m; image 2 covers mountain area, the resultant image is being checked. And stereo mapping test are undertaking.