| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1999 ---> Poster Session 6 |
The Macroscopic Effect of
Remote Sensing Geoinformation and Mineral prospecting
Qizhong Lin, Suhong Liu,
Linhai Jing and Jianwen Ma
Institute of Remote Sensing Application, CAS
P.O.BOX 9718, Beijing 100101
Abstract
Institute of Remote Sensing Application, CAS
P.O.BOX 9718, Beijing 100101
The macroscopic effect of remote sensing Geoinformation is one of the important properties of remote sensing information. The excellent macroscopic capacity feature helpful to research on geosciences objects.
Comparing to the big capacity of different remote sensing resolution scales, the levels of comprehensive application of remote sensing information are relatively low. It is a common thought that remote sensing information only complements common Geoinformation p[partly and remote sensing techniques do the same thing to common exploration methods. At present, with the development of new spectral imagery and Radar imagery techniques, NM-level object spectral features and various kinds of modular space structure information may be identified from the imageries. People are willing to find deposits directly, while ignoring the research on macroscopic effect of remote sensing. The Earth System is of a complex macroscopic knowledge system, space information system is of a typical layer and network frame, and macroscopic effect is central for the Earth system science. In recent years , there come the research fun of large-super-large ore deposits, the research fun of the relationship between large scale mineralizing and large scale mineralizing collecting areas, and the prominent research fun of mantle plume. All the funs about middle-large scale structure and mineralizing, relative to the Earth movement , are have intense relation with the macroscopic Geoinformation. To study the physical principles of the macroscopic effect of the remote sensing Geoinformation and search for the effect's relation ships with regional mineralizing is challenging topic and development trends of present solid resource remote sensing.
Introduction
With the development of remote sensing (RS) technology, the RS of mineral resource has revolved more deeply. For a long time, people have been customary to the programs of geological remote sensing, such as RS data collection, image processing, image enhancing, explanation, field test, and applied RS tech. To each stage of mineral resource exploration in order to help mineral prospecting. It is a helpful method to overlay three kinds of information, RS, geophysics and geochemist information. But the comprehension and the application of RS information are far less that the ability of RS technique, which is usually regarded as one kind of compliment to the routine Geoinformation and exploration methods. Especially, with the new development of sensors, NM-level object spectral features and various kinds of modular space-structure information may be obtained by spectral imagery and Radar imagery techniques, even alterative minerals may be identified from the imageries. People are willing to find deposits directly , while ignoring the research on macroscopic effect of RS. Ore deposit does not exit along, mineralizing does not exit in part region along, and each mineralizing element, as one kind of mineral in the earth participates in global structure movement and mineralizing function with other elements. Apart from to adopt modern Earth observation techniques fully , to collect microscopic rock and mineral information, and to study microscope substance composition principles, the study of mineral resource RS should be dig full large-space-scale metrication Geoinformation deeply , and to build application theories, techniques and methods of the specialty. There are a few samples of studying global structures and ore distribution by using space fight RS information. What's more, at recent years, there comes the research fun of large -super-large ore deposits, the research fun of large scale mineralizing and large scale mineralized collecting areas, and the promineralized collecting areas and the prominent research fun of mantle plume. All the funs about middle-large scale structure and mineralizing, related with the Earth movement, area have intense relation with the macroscopic Geoinformation. To study the physical principal of the macroscopic effect of the RS Geoinformation . To study the physical principals of the macroscopic effect of the RS Geoinformation and search for the relationship of the effect with regional mineralizing is challenging topic and developing trends of present solid resource remote sensing.
1. The Double phenomena of the space Feature of RS information
It is a common thought that the resolution of RS is the key discriminate object . The higher the resolution, the stronger the ability to solve problems. Therefore, apart from both to enhance spectral and space resolution, and to improve imagery spectral technique and high-resolution Radar space techniques, men are devoted to the study of decompose-pixel technique. Modern RS may be regarded as a pixel-detecting technique, based on detecting units. Some researchers are trying to apply some physical principles on basic particles to interpret RS physical principles, then to build pixel-scale RS basic theories and system of RS techniques and method, supported by present RS techniques and method on information obtainment, image processing and information extraction. While, the RS system are facing on challenge from the mineral resource RS exploration. It is an undeniable fact that while the RS resolution has been enhanced greatly, while there are no breakout on exploration theories, technical method and exploration effects of mineral resource RS. One reason of the fact is due to the microscopic and macroscopic effects of RS information, called the double effects of RS information, The later effects is usually ignored in the common study, while the former is weighted. But, in accordance with the similarity in both the space scale and time scale of the macroscopic effects of RS and the mineralizing function, the macroscopic effect is more suitable to macroscopic exploration study.
Microscopic Effect: All substance on the Earth is composed of kind of rocks and minerals. When using RS data, man pays more attention to minerals information then to rock information. For, in space scale, minerals are more attention to mineral are more approximate to microscopic particles, molecules, atoms, ions, electrons, the physical properties and the spectral properties of which may be used to study the microscopic principles of rock compose and to build feature spectrum database for discriminating minerals. Pixel-spectrum decomposition technique can decompose each end number to sub-pixel scale, and present rock properties in precise approximation to the weight of each end number. Imagery spectrum technique has unified mineral images and the corresponding spectrums, using spectrum match to discriminate mineral directly in the spectrum dimension. All the theories and method based on pixel scale objects, embody the macroscopic effects of RS information space.
Macroscopic Effect: The macroscopic effects of RS information is obvious. If a little-scale image is compared to a reduced big-scale image of the same area it is easy to find that two images represented the same object are not same completely. For example, in kinds of RS imageries, it is difficult to find the imagery feature, corresponding to a structure trace shown clearly on NOAA imagery. The trace is difficult to be found in middle-scale TMs scenes. It is nearly non-existing on large-scale aero-RS imageries. Stratums of various rocks may appear as one imagery of similar hue. Directly heterogeneous rocks appear as imageries of the same hue and texture. Such phenomenon is normal in the nature. We may simulate such thing on computer: use randomly various spectrums of objects as background, object information is added (an irregular white spot), then change the scale of the image gradually, and object information is shown more obviously. In figure (a), the irregular white spot is similar to letter c, and is overlaid by a cross form; while the form of letter c has been similar to a polygon in figure (b), and become a punctual white spot. In such an experiment, the shrinking of image scale is largely equal to the changing of space measure, suppressing high frequency noise and enhancing low frequency information. The experiment shows that the macroscopic effect of RS information is actually existing.

Figure 1 A simulation experiment of macroscopic effect of RS information
Having studied the BRDF property of vegetation, Xiaowen Li found that some physical principles of electromagnetic wave, for instance, Beer principle, had been unavailable when the proportion of RS resolution and the measure of vegetation leaf surface, in addition to vegetation spacing, changed. So, he believes there is a 'measure effect' problem of electromagnetic wave of object, which has been proved by Li-Strahler Model that object in pixel-scale space is a Lombard object, or not a Lombard object in a larger space than pixel scale (Xiaowen Li, 1999)1 [1]. All above shows that various scale RS information has various spectral features; the macroscopic and microscopic effects are two sides of object properties and can not be obtained by simple composition or decomposition progress.
2. The physical Principles of Macroscopic Effect
The Macroscopic effect RS information may be explained by the interference property of electromagnetic wave: if there is frequency wave v made up of a plenty of homochromatic waves, between v0 to v0+Dv, random overlay of each part may result in change of composing field.
Definition: After a Dt interval in interference time, there is a circle between waves v0 and v0+Dv:
the definition of inference length is :
If there is systematic relationship between two waves of radiant point, which are interfered, and the extent of composed wave is between the sum and the difference of them. Say mathematically, if E1 (t) and E2 (t) are two part field, composed field is
Average power is :
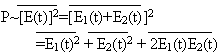
If two waves are not interfered, then,
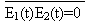 and
P=P1+P2 : if do,
and
P=P1+P2 : if do, 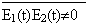 To the later,
To the later,
P<P1+P2 (at some places)
P>P1+P2
P>P1+P2 (at the other places)
In a word, the sum of two interfered part fields may larger than that of each of them. Obviously, many faint radiant points may bring out much stronger signs of composed field. The theory may be used to explain the reason why radiantly faint points may be clearly shown in RS imageries. For another sample, in order to explain the very brightness of plenilune, people firstly explain by geometrical optic principles that the shadow of high objects affects the brightness. But after measuring the spectral reflectance of soil samples brought back from the Moon by Apollo, man found that the brightness could not completely result from the reflectance. By measuring the change of the ratio of linear polarization and rotated polarization according to the direction change of observation, Hapke proved that interference enhance in NM-space is the true contribution to the brightness of plenilune.
2. The Geo-comprehensive and model of Macroscopic Effect.
The earth space information is a huge knowledge systems with typical various grid structure. RS information also has time, preciseness and uncertainly property. The feature information is very important. The experiment above shows that many traces and geological elements have great linear correlation with environment. The interference of various scales can expose the slightly and consistence property of various geological events, Spectral and space properties are shown in RS information. The result of a geological event (mineralizing functions), is a complex function of type, proportion, size , form, the kinds of space distribution combination and density. There may be a function [2].
In the function, is a index of spectral feature and may be regarded as a function f of type, proportion (m), size (s), form(h), space distribution direction (s) and space density (o).
The function represents the common comprehensive of knowledge elements of RS information: spectral feature (Hue)-object ingredients, space feature (texture)-structure (sh, s, o, p). There exist kinds geometrical relationship in respect to their distribution. RS information structure system of mineral resource modeled by object comprehensive is as follows (Figure 2).
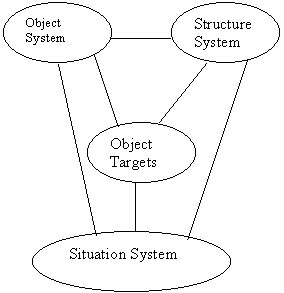
Figure 2. The RS Information System of Solid Mineral Resource.
RS information is made of three-sub-system information: object ingredient, structure(texture) and situation (relative place and geometrical construction). Object ingredients refer tot the object ingredients of the earth, including stratums, rocks, minerals and alluvium. Structure system refers to kinds of space structure of objects in the earth, including fracture, cranny and topography. Situation system includes ingredients, space situations of structures, combination and space constriction relationship etc, which are all controlled by geological principles.
Each of the three sub-systems is independent and relative to the others. The various scale series in or between the sub-systems form the complex level net structure of RS space information. As shown in figure 2, spectral features and space features of RS information, two basic elements of RS imageries, may be measured quantitatively or half-quantitatively and are the main feature information measured and dealt with by RS techniques. Situation features belonging to geographical knowledge, can not be operated by present RS image processing techniques. Each part of the three sub-systems is indispensable element for describing the features of geological events, to build up corresponding RS identification spectrums made up of color (Hue)- from (structure)- event (background), and to integrate all kinds of relative geological information, obvious or faint, whole or fragmentary, direct or indirect and then to expose geological principles in the elements. The double effects of the information space properties of RS, similar to the relationship of the specialty and common specially of an object showing the two sides of an object, showing the two sides of an object, results in two exploration research methods. For the various geological objects and phenomenon the microscopy research of RS information emphasizes on the composition, an isotropic property, mineralizing alteration and other concrete properties of object belonging to analysis methods. On the contrary the Microscopic effect research of RS information, based on the research on the macroscopic properties of kinds of geological elements (targets), obtains integrated properties of higher levels, in addition tot the relationships of kinds of geological elements, belonging to comprehensive methods.
4. Mineral Prospecting of Microscopic Effect
As mentioned above, the macroscopic effect of RS information enhances diffused faint information of targets and shows it off. In the same way, it may enhance the information transferred from deep earth. For example, at present, man is not very clear about the reasons why some old river ways buried in sediments of 600-meteer depth show off in MSS imageries. But the interference and overlay of comprehensive information is undeniably one reason of it (Shupeng Chen, 1998) [3]. The Macroscopic effect of RS information is very useful to geological exploration, for one deposits, often insidious or half insidious, show the edge of ore deposits or altered peripheral rocks on ground surface. Alteration changes either the physical state or the chemical state of rocks, or both. Especially, large-scale mineralizing happened on in deep earth must function in a large range space, form large planar orbicular or zonal faintly altered diffusion belt. Such large-scale space, of interference information field only can be exposed by the macroscopic effect of large-scale RS information. The anchor has used the Microscopic effect of NOAA imageries to study the macroscopic geological features of the large-scale ore deposits of Tianshan Mountain in the Middle Asia, found some deposit clustering principles of large-scale space and obtained excellent exploration results [4].
Study on Macroscopic Deposit-clustering Principles
- Detecting Mineralizing Structure Background of Deep Earth.
An available mineralizing structure background is one indispensable condition of large-scale deposits. The mantle upheaval, magma invasion, volcano-volcanic vault, density change resulted from matter exchange and other cases, all have imitate relationships with the thermal-dynamical environments in the earth and are a reflection of deep deposit clustering. In the transferring process of deep earth information, each element interacts with others is being overlaid or filtered then form hue and structure abnormally in RS imageries such as circle features in imageries. Another example, in NOAA imageries, the Muluntau gold deposit is shown as a ring of near 100-kilometer in diameter overlaid by a group of vertical transfer-structures, which may be the reflection of the thermal-dynamic background of insidious rocks in deep earth.
- Detecting 'Transferring' structure
"Transferring" structures refers to a thin belt, a tense strain belt and strain-releasing field of stress function of the earth, or a highly penetrative gate, controlling the movements of magma, mineralizing fluid, oil and gas, and thermal flu, or other actions, such as metamorphosis and earth-quakes. It is an important many tiny and dense linear structure, diffused and faint edges, outcrops of variable width from several to tens of kilometers, range from tens to hundreds of kilometers, even near thousand kilometers. On the earth surface, accidentally, it presents as linear permutation of weathered or eroded canyons, irregular up heaved terrains or other forms. Only according to the macroscopic effect of RS information, it harmoniously show up and is effectively identified out. Anchor found that all super-large-scale deposits of Tianshan Mountain in the Middle Asia were relative to 'transfer' structures.
The 'Background + events' Mineralizing Analysis Method is fashionable and very effective. It decomposes RS information into two basic kinds, say, mineralizing background information and mineralizing event information, which represent different mineralizing geological functions of two geologically time-space principles. Mineralizing function is a long time process. For example, regarding light-level metamorphosed rock series as background information which have altered peripheral rocks and regard it as mineralizing event information, then found RS exploration targets of large-scale ores, which has been proved the extent of 'China gold belt' in Kunlun Mountain.
Conclusions
- The macroscopic and microscopic effects are the two basic properties of RS information, relative and independent to each other. They cannot be obtained through simple composition or decomposition.
- The macroscopic effect existing objectively is the result of interference overlay of the information of faint radiant points.
- The macroscopic effect is the capable of identifying interfering information field of faint objects, exposing geological principles of large-scale, and enhancing the research on large-scale mineralizing function.
- Xiaowen, Li, BRDF of vegetation, "the earth system science", Chinese science & tech. Press, 1998, p-181.
- A. W. Siegrist & C. C. Schnetyler, The best identification bands of rocks, transferred from "photogr. Eng. Rem. Sem." Vol. 46, No.9, 1980, Collection of RS, Part II "Image processing and geological applications", Institute of information, the ministry of Geology., Beijing, Geological press. 1982.
- Shupeng Chen, 1998, the exploitation and applications of RS information, "the earth system sciences", Chinese science & tech. Press, p-203.
- Qizhong Lin, 1995, the practice and expectation of RS exploration, "the new development of RS science", Science Press, 1995, p-301-305.