| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1999 ---> Poster Session 3 |
Digital Photogrammetric
Workstation On Windows NT
Abstract
In this paper, A Digital Photogrammetric Workstation (DPW) on Windows NT which can be used in city planning is brought forward Much new technologies such as image auto-match, computer vision, graphics and image processing are adopted. This system can be applied in large scale digital mapping black and white/color Ortho-image making, city 3D model rebuilding and data of 3D city GIS acquiring / update. It is very effective tool for processing city spatial data.
A Digital Photogrammetric Workstation comprises the computer system stereoscopic display device, 3D measurement device, I/O device and correspond software (Shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2). In the following we’’ll explain the make –up and design of this system through hardware system and software system in detail.
1. The make-up and design of hardware systems
Hardware system consists of the computer system high refresh rate and large screen monitor (dual monitor) Stereoscopic display device, 3D measurement device, I/O device. Their installations are as follows:
(1)The installations of computer system are as follows:
(2)Stereoscopic display device
(3)3D measurement device
(4)I/O device
All of the devices and apparatus above are of standard making with the exception of 3D measurement devices and control emitter which are produced by our own research institute.

Figure1 : DPW photo
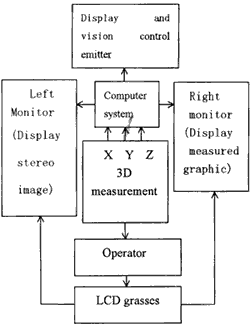
Figure 2 DPW Logical Frame
The whole system consists of nine model. There are original information control, digital image orientation, DEM extraction, object collection, graphic edit, topographic import, digital aerial triangulation, ortho-image making and 3D model rebuild. The whole system is developed by VC++5.0 in Windows NT 4.0 environment. The make-up of the software system is shown in Figure 3.
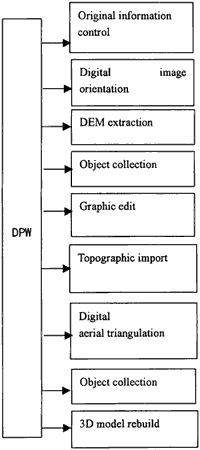
Figure 3 DPW Software Model
3.The conclusion
The system have already been put to use in business and it can accomplish the making of different-scaled digital topographic, ortho-image and 3D perspective view. It will be widely used in survey and mapping, forestry, agriculture, geology, medicine science, city programming work, and education etc.
Reference
- Tag Liang and Christian Heipke: Automatic Relative Orientation of Aerial Images, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol. 62, No. 1 (1996).
- Eugene E Derenyi. The Digital Transferscope, Photogrammetrci Engineering and Remote
- Sensing,Vol. 62, No. 6 (1996)
- Charles K. Toth and Amnon Krupnik Concep, Implementation, and Results of an Automatic Aerotriangulation System, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol. 62 No.6 (1996)
- Peggy Agouris and Toni Schenk: Automated Aerotriangulation using Multiple Image Multi-point Maching, Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol, 62 No. 6(1996)
- Christian Heipke: Automation of interior, relative and absolute orientation, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 52 (1997)
- J. Shan An algorithm for object reconstruction without interior orientation, ISPRS Jouranl of Photogrametry and Remote Sensing, 51 (1996).
- Li Deren and Shao Juliang: The wavelet and its application in image edge detection, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 49(3) (1994)
- M. Sinning-Meister, A. Gruen, H. Dan: 3D City models for CAAD supported analysis and design of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 51 (1996)
- Emmanuel P. Baltsavias: Digital ortho-image-a powerful tool for the extraction of spatial and geo-information, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 51 (1996)
- Toni Sckenk (1996): Current Status and Future Directions of Digital Photogrammetry: A Personal View, PE&RS June (1996)
- Kenert Torlegarel (1996): Status, Prospe cts and The Profession. PE&RS June (1996)
- Lan Dowman (1996) : Market and Economics of Digital Photogrammetric System. PE&RS June (1996)
- Edward M. milhai (1996): From the Kelsh to The Digital Photogrammetric WorkStation. PE&RS June (1996)