| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1999 ---> Geology |
Feasibility to monitor
Changbai Mountain volcanic activities by space techniques
Bo Liqun, Hua Renkui
Changchun Institute of Geography
Chinese Academy of Science, Changchun, P.R.China, 130021
E-Mail:geoinfo@public.cc.jl.cn
Changchun Institute of Geography
Chinese Academy of Science, Changchun, P.R.China, 130021
E-Mail:geoinfo@public.cc.jl.cn
Keywords: volcano monitoring, abrupt geothermal
anomaly, thermal infrared remote sensing
Abstract
Volcano eruption is one of the most serious geological disasters, however, a host of facts have proven that Changbai mountain volcano is a modern dormant active volcano and had ever erupted disastrously. With the rapid development of space technology such as RS (Remote Sensing) technology, GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology and GPS (Global Positioning System) technology, monitoring of volcano activity has already become feasible. The paper presents a method by which volcano activities would be monitored, that is, RS measures geothermal anomaly, GIS analyzes volcano distribution and activity pattern, and GPS monitors the micro-deformation of crust (totally called ‘3S’ technique). Reasons for Abrupt geothermal anomaly is mainly analyzed, and transmission mechanism of geothermal anomaly in volcanic regions are explained in detail.
1. Introduction
Changbai Mountain volcano is the biggest one in China, and one of the famous volcanoes in the world, ever greatly erupted 1200 years ago, last eruption in about 1903. Based on its frequent modern eruption activities, complicated magma components, huge volcanic base, high volcanic cone, various eruption types, Changbai Mountain volcano has become a dormant active one with a potential eruption danger.
The region is an important economic development zone of Jilin Province in China, especially in many aspects of resources such as tourism, energy, terrestrial heat, medicine herbs, forestry and minerals, it has huge development potentialities. However, this type of very dangerous volcano existed have to draw an attention of all level of governments, investors and scientists. For this reason, many scientists did a large number of research jobs in the fields of volcano geology, volcanic kinetics, volcanic eruption materials, volcanic magma and magma movement in decades. In other way, they applied various devices to measure and monitor the variation of geophysics and geochemistry, for example, earthquake, geomagnetism, ground temperature and crust deformation. With the development of space technology, especially remote sensing and global positioning system, monitoring volcanic activities of Changbai Mountain from the space has become possible, mainly concentrating on geothermal anomaly, geomagnetism anomaly and crust deformation. This paper discusses thermal infrared satellite remote sensing technique applied on volcanic activities of Changbai Mountain.
Thermal infrared detecting technology is to use thermal infrared sensor to record the data reflected by heat objects. After correcting the data and removing noise interference, we can obtain the temperature difference between abrupt geothermal anomalous area and normal area, and further analyze volcanic activity trend.
2. Principles of remote sensing monitoring for abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
2.1 Feasibility of remote sensing monitoring for abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
Abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region comes out in the forewarning period of volcano eruption or violent volcanic activities. This type of anomalous geothermal is able to emit electromagnetic wave by the way of various transmissions, and accepted by thermal infrared sensors. Based on the formation transmission of abrupt geothermal anomaly, geothermal anomaly in volcanic region should be occurred in a large area up to about a few thousand kilometers; the temperature rises up to 6 degree centigrade, more obviously in the area of fissures or low valleys.
2.2 NOAA satellite and AVHRR data
In general, abrupt geothermal anomaly caused by volcanic activities may last a few hours or days, therefore, high temporal meteorology satellite has to be used as an ideal monitoring base. AVHRR data has 5 channels, in which there are two thermal infrared channels; one middle infrared channel; another two as reflective channels. NOAA satellite uses dual-satellite system so that the same place is taken at least 4 times every day. Its ground resolution of AVHRR data on the nadir point is 1.1 kilometers; recorded values are 8 byte, which can represent the range of temperature from the lowest to the highest on the earth’s surface. These features may fully meet the need of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Figure 1 shows the whole flow chart of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano by meteorology satellite
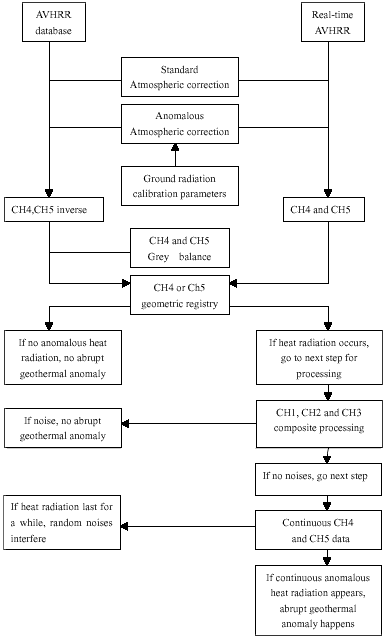
Fig. 1. Flow chart of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano by meteorology satellite
2.3 Advantages of monitoring by meteorology satellite
The surveying coverage of meteorology satellite is very wide, 2800km for a single orbit, an effective distance is about 1000km. A receiving station can cover 4500km wide and 14 million square kilometers in area, which is very useful to analyze the crust movement and the magma activity behavior for a large area, and enhances the accuracy of preceding volcanic eruption.
3. Feature of abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
According to the now generally accepted “plate-tectonics” theory, scientists believe that the Earth’s surface is broken into a number of shifting slabs or plates, which average about 50 miles in thickness. These plates move relative to one another above a hotter, deeper, more mobile zone at average rates as great as a few inches per year. Most of the world’s active volcanoes are located alone or near the boundaries between shifting plates and are called “plate-boundary” volcanoes.
Also, volcano emanation is a form of strong release of substance and energy inside the Earth. When cold oceanic plates go down to one side of island arc from oceanic trench, during the initial period, volcanic activity could not be caused in virtue of low temperature. Crush materials melt under the action of various stresses at a specified distance and depth of the plates (You et al., 1998). Thus, melting substances will erupt from rock faults or rupture belts under the action of high pressure (Song et al., 1990; Jin et al., 1994). During the development of volcano, abrupt geothermal anomaly definitely occurs at repeated times, however, pocket of magma detained at shadow crush is only the ideal spot hot source of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Deep melting magma in the course of moving up by high pressure excites pocket of magma. Therefore, the existed anomalous subterranean heat is aroused into abrupt geothermal anomaly. Different types of volcanoes have different geothermal features. Studying different types of geothermal features and intensity of volcano activity is one of thermal infrared remote sensing monitoring and forecasting.
The newer age and the bigger scale of volcanic activity is, the more possible the formation of high temperature anomaly. From the view of global, dejected or expanding acid volcanoes are interrelated with the high temperature water-heat system, but not slab basic volcanoes do. This is because rocks erupted by basic volcanoes have vanished by the remaining heat of rock bodies. Pocket of magma necessary to form the high temperature water-heat system is not held up in the crushed shadow of volcanic region, so that there is not a direct heat source to increase ground temperature. The volcanic region at Changbai Mountain fully reflects this feature. The volcano of Changbai Mountain erupted mainly on crack; since 2 Ma, it has changed into central acid eruption, and pocket of magma would be found at 15km depth of heavenly pool. The characteristics might become an ideal condition providing to forecast the abrupt geothermal anomaly prior to volcano eruption.
4. Analysis of transmission mechanism of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
The deep terrestrial heat in volcanic region might be transmitted to surface through various transmission mechanisms. During the dormant period of volcano, volcanic areas have a phenomenon of geothermal anomaly; while in mobile or forewarning period, geothermal anomaly would be more obvious than ever. In the course of transmitting to the surface, the deep terrestrial heat mainly transmits through electromagnetic radiation, conduction of terrestrial heat, convection of terrestrial heat etc. towards the surface, which makes the terrene’s temperature rise. Besides, solar radiation also has a certain role on the surface temperature rising.
4.1 Solar Radiation
In days the surface of earth radiated by the Sun makes its temperature rise. In the forewarning period of volcano activity, substance structure and state will be changed because of geothermal anomaly. The temperature in anomalous region is higher than in normal region by solar radiation. This is because a great deal of high temperature’s magma goes up to crush and heats country rocks. Vapors in country rocks and soils greatly evaporate. When they meet chilled junction in the surface, it will make the content of water in substance increase, which can change the structure of water layers of soils and rocks, and get heat capacity of substance larger. This shows that substances are very capable of storing heat. There is an obvious difference for the temperature indicator between anomalous and normal areas.
4.2 Conduction of terrestrial heat
Surveying shows that fissures and pocket of magma exist in the Changbai Mountain region, which can provides a great deal of substance source and dynamic source stored up as huge heat energy for volcanic activities. So geothermal anomaly often occurs in the region of modern volcanic activity. Geothermal anomaly is the phenomena that underground temperature and geothermal gradient increases much more in the area than its surroundings. Geysers and hot springs are generally found in above regions. During the violent volcanic activities or forewarning period of volcano eruption, abrupt geothermal anomaly comes out. Abrupt geothermal anomaly means that underground temperature on some spots as well as the affected temperature of surrounding area abruptly increases in a short time. Its geophysical properties represent time and space features of current subterranean magma activity or crush movement intensity in the area, which contains much information for geology, geophysics and geo-dynamics. So the above information is very important to monitor and forecast temporary volcanic activity.
During the development of volcano, abrupt geothermal anomaly definitely occurs at repeated times, however, pocket of magma detained at shadow crush is only the ideal spot hot source of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Deep melting magma in the course of moving up by high pressure excites pocket of magma. Therefore, the existed anomalous subterranean heat is aroused into abrupt geothermal anomaly.
4.3 Convection of terrestrial heat
Most geothermal energy can be convected through the underground water and the magma motion. When hot sticky magma suddenly touches cold circulation layers it will produce a great deal of volatile flux and underground water will be heated. In addition, while volcano activity is active, the temperature of original hot spring and crater lakes must be rising. In this case, heat transmission in water body mainly depends upon heat exchange. Produced volatile flux and heated gases such as vapor, hydrogen, HCL, CO 2 , CO, H2 S, SO2 , HF etc contained in magma and adjoining rocks will be released to air through movement faults and broken rock cracks. They not only bring heat to surface, but also result in the hothouse effect in basin and low gully, which will make temperature rise in the area.
In summary, experiments prove that according to the above transmission mechanism, there is an obvious increase for surface’s temperature in abrupt geothermal anomalous area in contrast to geothermal normal area during the forewarning period of volcano activity. In the view of formation cause and geothermal transmission mechanism of abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano, rising range of temperature in anomalous area could be from 3 to 6 degree centigrade or more. This offers a basic condition for monitoring volcanic activities by thermal infrared remote sensing techniques.
5. Conclusion
Volcano monitoring involves the recording and analysis of volcano phenomena. The rapid development of space technology offers scientists a good chance of conducting a serial of remote sensing technique researches. Meteorology satellite as a popular surveying device is a ideal tool to monitor abrupt geothermal anomaly during the forewarning period of volcanic eruption. Changbai Mountain volcano located in Jilin Province has been studied by both chinese scholars and foreign scientists for a long time. At present, except meteorology satellite monitoring, global positioning system (GPS) is also used to monitor crust deformation behaved before eruption.
References
Abstract
Volcano eruption is one of the most serious geological disasters, however, a host of facts have proven that Changbai mountain volcano is a modern dormant active volcano and had ever erupted disastrously. With the rapid development of space technology such as RS (Remote Sensing) technology, GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology and GPS (Global Positioning System) technology, monitoring of volcano activity has already become feasible. The paper presents a method by which volcano activities would be monitored, that is, RS measures geothermal anomaly, GIS analyzes volcano distribution and activity pattern, and GPS monitors the micro-deformation of crust (totally called ‘3S’ technique). Reasons for Abrupt geothermal anomaly is mainly analyzed, and transmission mechanism of geothermal anomaly in volcanic regions are explained in detail.
1. Introduction
Changbai Mountain volcano is the biggest one in China, and one of the famous volcanoes in the world, ever greatly erupted 1200 years ago, last eruption in about 1903. Based on its frequent modern eruption activities, complicated magma components, huge volcanic base, high volcanic cone, various eruption types, Changbai Mountain volcano has become a dormant active one with a potential eruption danger.
The region is an important economic development zone of Jilin Province in China, especially in many aspects of resources such as tourism, energy, terrestrial heat, medicine herbs, forestry and minerals, it has huge development potentialities. However, this type of very dangerous volcano existed have to draw an attention of all level of governments, investors and scientists. For this reason, many scientists did a large number of research jobs in the fields of volcano geology, volcanic kinetics, volcanic eruption materials, volcanic magma and magma movement in decades. In other way, they applied various devices to measure and monitor the variation of geophysics and geochemistry, for example, earthquake, geomagnetism, ground temperature and crust deformation. With the development of space technology, especially remote sensing and global positioning system, monitoring volcanic activities of Changbai Mountain from the space has become possible, mainly concentrating on geothermal anomaly, geomagnetism anomaly and crust deformation. This paper discusses thermal infrared satellite remote sensing technique applied on volcanic activities of Changbai Mountain.
Thermal infrared detecting technology is to use thermal infrared sensor to record the data reflected by heat objects. After correcting the data and removing noise interference, we can obtain the temperature difference between abrupt geothermal anomalous area and normal area, and further analyze volcanic activity trend.
2. Principles of remote sensing monitoring for abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
2.1 Feasibility of remote sensing monitoring for abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
Abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region comes out in the forewarning period of volcano eruption or violent volcanic activities. This type of anomalous geothermal is able to emit electromagnetic wave by the way of various transmissions, and accepted by thermal infrared sensors. Based on the formation transmission of abrupt geothermal anomaly, geothermal anomaly in volcanic region should be occurred in a large area up to about a few thousand kilometers; the temperature rises up to 6 degree centigrade, more obviously in the area of fissures or low valleys.
2.2 NOAA satellite and AVHRR data
In general, abrupt geothermal anomaly caused by volcanic activities may last a few hours or days, therefore, high temporal meteorology satellite has to be used as an ideal monitoring base. AVHRR data has 5 channels, in which there are two thermal infrared channels; one middle infrared channel; another two as reflective channels. NOAA satellite uses dual-satellite system so that the same place is taken at least 4 times every day. Its ground resolution of AVHRR data on the nadir point is 1.1 kilometers; recorded values are 8 byte, which can represent the range of temperature from the lowest to the highest on the earth’s surface. These features may fully meet the need of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Figure 1 shows the whole flow chart of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano by meteorology satellite

Fig. 1. Flow chart of monitoring abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano by meteorology satellite
2.3 Advantages of monitoring by meteorology satellite
The surveying coverage of meteorology satellite is very wide, 2800km for a single orbit, an effective distance is about 1000km. A receiving station can cover 4500km wide and 14 million square kilometers in area, which is very useful to analyze the crust movement and the magma activity behavior for a large area, and enhances the accuracy of preceding volcanic eruption.
3. Feature of abrupt geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
According to the now generally accepted “plate-tectonics” theory, scientists believe that the Earth’s surface is broken into a number of shifting slabs or plates, which average about 50 miles in thickness. These plates move relative to one another above a hotter, deeper, more mobile zone at average rates as great as a few inches per year. Most of the world’s active volcanoes are located alone or near the boundaries between shifting plates and are called “plate-boundary” volcanoes.
Also, volcano emanation is a form of strong release of substance and energy inside the Earth. When cold oceanic plates go down to one side of island arc from oceanic trench, during the initial period, volcanic activity could not be caused in virtue of low temperature. Crush materials melt under the action of various stresses at a specified distance and depth of the plates (You et al., 1998). Thus, melting substances will erupt from rock faults or rupture belts under the action of high pressure (Song et al., 1990; Jin et al., 1994). During the development of volcano, abrupt geothermal anomaly definitely occurs at repeated times, however, pocket of magma detained at shadow crush is only the ideal spot hot source of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Deep melting magma in the course of moving up by high pressure excites pocket of magma. Therefore, the existed anomalous subterranean heat is aroused into abrupt geothermal anomaly. Different types of volcanoes have different geothermal features. Studying different types of geothermal features and intensity of volcano activity is one of thermal infrared remote sensing monitoring and forecasting.
The newer age and the bigger scale of volcanic activity is, the more possible the formation of high temperature anomaly. From the view of global, dejected or expanding acid volcanoes are interrelated with the high temperature water-heat system, but not slab basic volcanoes do. This is because rocks erupted by basic volcanoes have vanished by the remaining heat of rock bodies. Pocket of magma necessary to form the high temperature water-heat system is not held up in the crushed shadow of volcanic region, so that there is not a direct heat source to increase ground temperature. The volcanic region at Changbai Mountain fully reflects this feature. The volcano of Changbai Mountain erupted mainly on crack; since 2 Ma, it has changed into central acid eruption, and pocket of magma would be found at 15km depth of heavenly pool. The characteristics might become an ideal condition providing to forecast the abrupt geothermal anomaly prior to volcano eruption.
4. Analysis of transmission mechanism of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region
The deep terrestrial heat in volcanic region might be transmitted to surface through various transmission mechanisms. During the dormant period of volcano, volcanic areas have a phenomenon of geothermal anomaly; while in mobile or forewarning period, geothermal anomaly would be more obvious than ever. In the course of transmitting to the surface, the deep terrestrial heat mainly transmits through electromagnetic radiation, conduction of terrestrial heat, convection of terrestrial heat etc. towards the surface, which makes the terrene’s temperature rise. Besides, solar radiation also has a certain role on the surface temperature rising.
4.1 Solar Radiation
In days the surface of earth radiated by the Sun makes its temperature rise. In the forewarning period of volcano activity, substance structure and state will be changed because of geothermal anomaly. The temperature in anomalous region is higher than in normal region by solar radiation. This is because a great deal of high temperature’s magma goes up to crush and heats country rocks. Vapors in country rocks and soils greatly evaporate. When they meet chilled junction in the surface, it will make the content of water in substance increase, which can change the structure of water layers of soils and rocks, and get heat capacity of substance larger. This shows that substances are very capable of storing heat. There is an obvious difference for the temperature indicator between anomalous and normal areas.
4.2 Conduction of terrestrial heat
Surveying shows that fissures and pocket of magma exist in the Changbai Mountain region, which can provides a great deal of substance source and dynamic source stored up as huge heat energy for volcanic activities. So geothermal anomaly often occurs in the region of modern volcanic activity. Geothermal anomaly is the phenomena that underground temperature and geothermal gradient increases much more in the area than its surroundings. Geysers and hot springs are generally found in above regions. During the violent volcanic activities or forewarning period of volcano eruption, abrupt geothermal anomaly comes out. Abrupt geothermal anomaly means that underground temperature on some spots as well as the affected temperature of surrounding area abruptly increases in a short time. Its geophysical properties represent time and space features of current subterranean magma activity or crush movement intensity in the area, which contains much information for geology, geophysics and geo-dynamics. So the above information is very important to monitor and forecast temporary volcanic activity.
During the development of volcano, abrupt geothermal anomaly definitely occurs at repeated times, however, pocket of magma detained at shadow crush is only the ideal spot hot source of geothermal anomaly in volcanic region. Deep melting magma in the course of moving up by high pressure excites pocket of magma. Therefore, the existed anomalous subterranean heat is aroused into abrupt geothermal anomaly.
4.3 Convection of terrestrial heat
Most geothermal energy can be convected through the underground water and the magma motion. When hot sticky magma suddenly touches cold circulation layers it will produce a great deal of volatile flux and underground water will be heated. In addition, while volcano activity is active, the temperature of original hot spring and crater lakes must be rising. In this case, heat transmission in water body mainly depends upon heat exchange. Produced volatile flux and heated gases such as vapor, hydrogen, HCL, CO 2 , CO, H2 S, SO2 , HF etc contained in magma and adjoining rocks will be released to air through movement faults and broken rock cracks. They not only bring heat to surface, but also result in the hothouse effect in basin and low gully, which will make temperature rise in the area.
In summary, experiments prove that according to the above transmission mechanism, there is an obvious increase for surface’s temperature in abrupt geothermal anomalous area in contrast to geothermal normal area during the forewarning period of volcano activity. In the view of formation cause and geothermal transmission mechanism of abrupt geothermal anomaly in regions of volcano, rising range of temperature in anomalous area could be from 3 to 6 degree centigrade or more. This offers a basic condition for monitoring volcanic activities by thermal infrared remote sensing techniques.
5. Conclusion
Volcano monitoring involves the recording and analysis of volcano phenomena. The rapid development of space technology offers scientists a good chance of conducting a serial of remote sensing technique researches. Meteorology satellite as a popular surveying device is a ideal tool to monitor abrupt geothermal anomaly during the forewarning period of volcanic eruption. Changbai Mountain volcano located in Jilin Province has been studied by both chinese scholars and foreign scientists for a long time. At present, except meteorology satellite monitoring, global positioning system (GPS) is also used to monitor crust deformation behaved before eruption.
References
- You Yongxong et al, 1998. Monitoring earthquake’s forewarning field in the northwest of Yunnan Province by remote sensing techniques. Science Press. p340-345 (in chinese)
- Song Haiyuan et al, 1990. Study on the volcano geology of Changbai Mountain. Yanbian University Press (in chinese)
- Jin Bolu et al, 1994. Study on volcanic geology of Changbai Mountain. Northeast Korean Nationality Education Press p71-72 (in chinese)