| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1996 ---> GIS |
Preparation of Indicative
Land use Plans using GIS
J. Jayasinghe and W. M. M.
Priyanthi
Land use Policy Planning Division
Ministry of agriculture, Land & Forestry
Abstract
Land use Policy Planning Division
Ministry of agriculture, Land & Forestry
- The land use Policy Planning Division (LUPPD) is presently engaged in the preparation of Indicative Land Use Plans (ILUP) of Provincial/District and Divisional Secretary (D.S) levels using GIS. ILUP classifies the land according to the intensity of land use.
- This paper outlines the procedure adopted in preparing an indicative Land Use Plan for the Bulathinhala D.S. Division in the Kalutara District. (Western Province)
The major objective of the Indicative Land Use Plans are to draw attention to inappropriate uses of land, to highligh the environmental problems that could arise in continuing with present land uses and; to indicate opportunities for better and more intensive use of land. It is expectd that the plans will enable decision makers to provide at least some direction to the changes in land use taking palce at the district level.
At the start ILUP s were prepared manually by superimposing the soil types or slop clases on the undated and use map. This procedure was found to be very time consuming. Furthermore the accuracy of the plan depended on the skill of the cartographer. Because of the need to prepare a large number of plans for the country (all the D.S. divisions) within a reasonable period of time and with greater accuracy, it was decided to develop a computer based methodology to produce ILUP s quickly and accurately.
The methodology was initially developed for the Bulathsinhala D.S. division in the Kalutara District (western Province). This division was selected because the required data had been collected by the Surveyor General's (S.G.) office under the Planning Support Project.
2.0 System Used
The Hardware used comprised:
- Sun Sparcstation 20 workstation with 1 GB Hard Disk
- The Calcomp digitizer (A0 size)
- Techject color plotter (Ali size)
The available software of the LUPPD, ARC/INFO Unix version 7.0.3 was used for the do GIS activities.
3.0 Methodology
3.1 Data Used:
There kinds of data were used in this system.
- The digital data generated by the S.G. office on land use. (1:20,000 scale)
- Digital topgraphic data obtained from the S.G. office. (1:50,000 scale)
- The data on land use changes gnerated by the LUPPD. These data were gnerated by updating the land use map prepared by the S.G. office using a revised legend. (appendix 1)
1. the digital data provided by the S.G. Office were updated by utilizing the data on land use change generated by the Luppd.
2. A slope class map was prepared utilizing the digital data on topography (contours) generated by the S.G. Office. Six slope class were derived using DTM as follows:
| 1. | 0 - 8% |
| 2. | 8 - 16% |
| 3. | 16 - 30% |
| 4. | 30 - 0% |
| 5. | 40 - 60% |
| 6. | > 60% |
3. The slope class coverage was overlaid on the land use coverage using 'UNION' command.
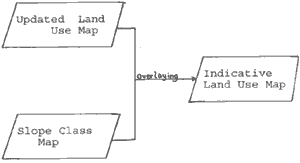
4. Land use intensity clases were derived by matching polygons in the land use coverage with the polygons in the slope class coverage. Four intensity clases were identified. (a) intensively used areas (b) semi intensively areas 9c) sparsely used areas (d) conservation areas. Each of the intensity classes were subdivided based on slope. These categories are indicated in appendix 2.
5. An AML (Arc Macro language) was prepared to print the map. (i.e. ILUP)
The ILUP for the Bulathsinhala D.S. Division was prepared using only the slope data because oher detailed data were not available. However it is hoped to use other physical and socio economic data wherever available to further refine ILUP s. such refinements will provide more detailed guidelines for the sustainable use of land resource in the country.
3.3. Conclusion
Misuse of land in many parts of the country has led to soil loses, lowering of productivity and decline in the natural eco-system diversity etc. It is very necessary therefore that measures be adopted to make the best use of the available land resources on a sustainable basis. Such sustainable use of course will depend on the preparation and availability of land use plans at the district and divisional level to guide the decisions of both policy makers and users of land. Such plans however cannot be prepared manually because they are needed urgently. The procedure outlined above enables the preparation of ILUP s quickly and more accurately. It also makes updating of the plans much easier as more detail permits easy retrieval of specific data as and when required by policy makers, planners and land users.
| Land use (1995) - Bulathsinghala D.S. Division | |
| Main Land Use | Sub Units |
| Paddy | Paddy (Rainfed) Paddy (Irrigated) Paddy (abandoned) Paddy with Seasonal Crops Paddy with one season cultivated |
| Tea | Tea (Seedling) Tea (V.P.) Tea (Abandoned) Tea (Seedling) - Less than 75% crop cover Tea (V.P.) Less than 75% crop cover |
| Rubber | Rubber (Mono Crop) Rubber with intercrop Rubber (Abandoned) Rubber (Monocrop) Rubber (Monocrop) - < 75% crop |
| Coconut | Coconut (Monocrop) Coconut with intercrop Coconut with livestock Coconut (Monocrop - < 75% crop cover) Coconut with intercrop - < crop cover) Coconut with intercrop - < 75% crop cover Other Plantation Cinnamon Banana Mixed Other |
| Homegarden | Homegarden (Mixed) Homegarden with tea (seedling) Homegarden with tea (V.P.) Homegarden with Rubber Homegarden with Coconut Homegarden with Cinnamon Homegarden with Banana Homegarden with Mango Homegarden with Coco |
| Market Garden | Market Garden |
| Builtup Area | Builp Area |
| Forest | Dense Forest Open Forest Forest Plantation |
| Grassland | Grassland - natural Grassland - improved |
| Chena | Chena |
| Scrub | Scrub |
| Distorted Surface | Distorted Surface |
| Barren Land | Barren Land |
| Marsh | Marsh |
| Rock | Rock |
| Water | Water |
| Indicative Land Use Plan | ||
| A. | Intensively Used Land Land Use Categories | |
| Paddy, both irrigated and rained; tea, seedling and VP: rubber inter-cropped; coconut, inter-cropped and mixed with livestock; in case plantation corps such as cinnamon, cocoa, cofee, cashew, citrus, mango lemongrass, banana, sugarcane, pineapple, etc., can be marked as already intensively used; if the crop cover if more than 75% forest, dense forest and forest plantations; grassland improved and natural; garden, hoem garden and market garden; built-up areas. | ||
| A1 | Area where present land use could continue with appropriate management to maintain the land cover | SLOPE(0-30%) |
| A2 | Area with should be used with conservation measure (seasonal corps are recommended only upto 40% | (30-60%) |
| A3 | Area recommended for forestry. Tree crops can be permitted only if strict conservation measure are adopted. | (>60%) |
| B. | Semi - Intensively
Areas Land Use Categories | |
| Rubber, mono - cropped; coconut, mono-cropped; other plantation crops such as cinnamon, cocoa, coffee, cashew, citrus, mango, lemongras, banana, sugarcane, pinapple etc., if the cropcover is less than 75%. | ||
| B1 | Area where land use can be intensified with minimal restrictions. | (0-8%) |
| B2 | Area where land use can be intensified with conservation practices. | (8-16%) |
| B3 | Areas where land use may be intensified with careful conservation in adopting suitable conservation practices | (16-30%) |
| B4. | Area where land use can be intensified with very strict adherence to conservation practices and good management (suitable for annual crops only upto 40%) | (30-60%) |
| B5. | Area recommended for forestry. | (>60%) |
| C. | Sparsely used Areas (Wet and
Intermediate Zones Only) Land Use Categories | |
| Paddy abandoned, tea abandoned rubber abandoned, scrub /chena, natural grassland, rockoutcropps, distorted surface and barren land. | ||
| C1 | Area where can be utilized for crop production, if the constrains could be rmoved economically and suitable conservation practices are adopted; can be used for on agricultural uses as well | (0-16%) |
| C2 | Area suitable for agro-forestry and tree crops with conservation | (16-30%) |
| C3 | Areas suitable for agro-forestry and tree crops with conversation | (30-60%) |
| C4. | Suitable for forestry | (30-60%) |
| C5. | Rockout crops and distorted surfaces falling under sparsely used category may be suitable for natural forest or extraction of gravel or for quarrying | ( >60%) |
| D. | Conservation Areas Land use categories | |
| Reservations, archaeological, forest, reserves, wildlife, parks &n sancturaries marsh/swamp, mangroves water bodies, and sand. | ||