| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1995 ---> Poster Session 3 |
Block Adjustment Method for
Mosaicing a Large Number of Satellite Image Data
Koki Iwao, Ryosuke
Shibasaki and Masataka Takagi
Institute of Industrial Science,
The University of Tokyo.
7-22, Roppongi, Minato-ku, Tokyo 106, Japan
Tel. +81-3-3402-6231 ext.2563
Fax. +81-3-3479-2762
E-mail : iwao@shunji.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Abstract Institute of Industrial Science,
The University of Tokyo.
7-22, Roppongi, Minato-ku, Tokyo 106, Japan
Tel. +81-3-3402-6231 ext.2563
Fax. +81-3-3479-2762
E-mail : iwao@shunji.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
This paper focused on the development of geometric correction method for mosaicing a large number of satellite data under the auspices of Land Use/Cover Change Study of South-East Asia(LUCS-ASIA).
In this project, we have to geometrically correct more than one thousand Satellite(Mainly Landsat TM & MSS, MOS-1 MESSER) scenes for three different years, i.e.1970's, 1980's and 1990's of South-East Asian region. If these images are geo-corded separately one by one, geometric distortions are likely to occur between different images.And it is not always easy to find enough GCPs in every scene. This makes the mosaicing of images labor-depending.In this paper, we propose a method to adjust geometric errors over all images at one time borrowing the idea of block adjustment in photogrammetry. Even if we can not find enough GCP points to one scene, we can adjust geometric errors over all images with the information of tie points between images.
1.Background and Objectives of the Study
Land use changes are becoming an important component for environmental, studies at all levels -local, regional and global. levels especially in South-East Asian regions. For a proper and complete understanding of the changes that are taking place in land use and their effects on the local, regional and global scales, we need to have a quality database of the landuses -both past and present, to help us in analyzing the changes on the time scale.
The Land Use / Cover Change Stud y of "South-East Asia(LUCS-ASIA) was taken up withan aim to develop uniform and standard timeseries database of the land uses by a core group among universities/National Institute of environmental Studies (NIES) in Japan under Fig.l Map Illustrating the the cooperation with research institutes/universities and governmental organizations in South-East Asian countries.
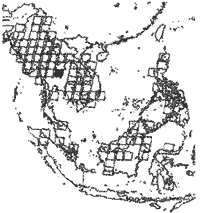
Fig.1 Map Illustrating the 100 Landsat Scenes
In this project, we have three main aims i.e.
- To generate time series mosaicing images around South-East Asia
- To generate land use/ cover time-series data set using satellite data
- To develop comprehensive GIS database
Here we focused on the method for mosaicing such a large number of data.
2 Methodology
So as to locate GCP's, we have to identify correspondence between feature points in images and those in topographic-maps such as DCW and World Data Bank. But there are so many images where typical geographic features such as river branch points and coastal lines which employs tie-points(TP} to conjugate neighboring images and conduct geo- cording of all images simultaneously. Even if we can get enough number of GCP data, these distribution may be so biased. We propose"Block adjustment method" for mosaicing large number of data. Even if we can not find enough GCP points and these distributions are not so much homogeneous, we can adjust geometric errors over all images. The process of the Block adjustment method for mosaicing large number of data are introduced in Fig 2.
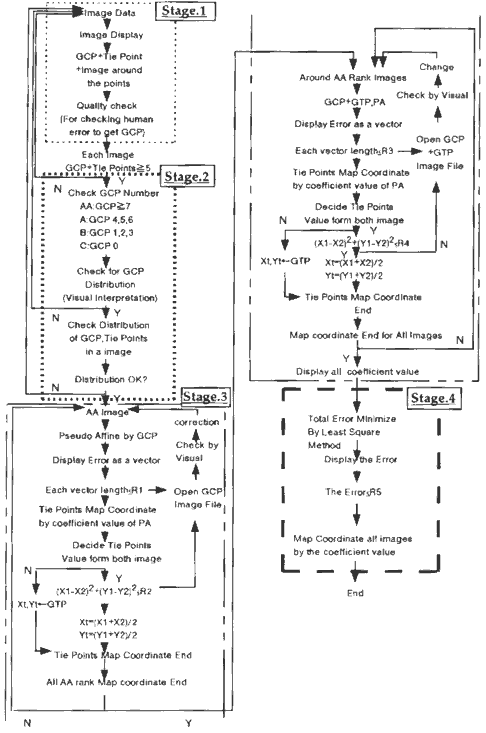
Fig.2 The Process for Mosaicing a Large Number of Satellite Image Data
We can divide this process for four stages
2.1 Measurin GCP and Tie oints for each Images
In this stage, we identify and measure coordinate values of GCP (image coordinate data ' and map coordmate data} and he pomts (Image coordmate data} for each Images. We use World Data Bank (coast and river data} to determine the map coordinate information for GCP.
2.2) Checking the Number and Distribution of GCP for each images
We use Pseudo Affine transform formula for geometric correction.
y=a5uv+a6u+a7v+a8
We need more than four GCP's to determine the parameters in this formula. And GCP points should be homogeneous. The number of GCP and these distribution have to be checked to avoid extreme bias in GCP / TP distribution over all images.
2.3 Settin the initial value of transform araI Mters for block ad.ustIMnt and detecting / eliminating gross errors
After checking the number and distribution of GCP points,
This stage also consists of four steps.
2.3.1} Calculate unknown transform parameters of "AA class" images (number of GCP~7} only from GCP
2.3.2} Compute map coordinate values of TP in AA class images
2.3.3} Replace TP with GCP in images overlapping / neighboring AA class images.
2.3.4} Calculate unknown transform parameters for the neighboring images (GCP<7}
By using the information of "geo-located" tie points, we can propagate initial geo- location of individual images from AA class image to neighboring "lower class" images. If any gross errors may be detected through these steps, we can evaluate the original image of GCP/TP .
2.4) Adjust geometric errors over all images with the information of tie oints between images
By using initial values of the transfer parameters of each images, geometric errors over all images are adjusted borrowing the idea of block adjustment in photogrametry to compute accurate values of the transform parameters.
3. Experiment
The block adjustment method is being applied to M05-1 MESSER images. The results will be present in the Conference.
4. Future Works
Automated identification / measurement of GCP's and TP's as to minimize human labour in GCP /TP measurement, we need to develop automated processing for identifying / measuring GCP's and TP's. For GCP identificate / measurements, feature-based matching will be employed while template matching techniques of image are applied to TP measurement.
References
- JARS,Remote Sensing Note, Nihon Printing Co.,Tokyo,I993 pp.178 -179
- Ryosuke Shibasaki, Masataka Takagi and Koki Iwao (1995), "Land. Use Change Study of South East Asia(LUCS-ASIA)", Proceedings of the International Symposium on Vesitation Monitoring International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Chiba, Japan, pp.199 -205
- K.S.Rajan, Koki Iwao,Ryosuke Shibasaki & Masataka Takagi (1994), "Semi-Automated, lassification System for Landsat Pathfinder Project", Proceedings of the 15th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Bangalore, India, vol.2 pp.L-6-1 -L-6-4