| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1994 ---> Forestry |
A Comparative Study on
Relationships between Forest and Soil Series upon Different Topographies
by GIS Technique at a Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot, Lampang
Province, Thailand
Manasanan Kantontong
Geographician(Cartographer) Technical Forest Bureau
Forest Resource Analysi is Branch Royal Forest Department
Bangkok, Thailand.
Manasanan Kantontong
Geographician(Cartographer) Technical Forest Bureau
Forest Resource Analysi is Branch Royal Forest Department
Bangkok, Thailand.
Abstract
A compartive study on relatonships between forest types, man-made activities and soil series upon different topographies was conducted at a mae huad demonstrative forest plot, amphoe ngao of lampang province in northern thailand. The purpose of the study is to make a forest Landcover map of a Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest plot which relates to the soil ser4ies appeareeupon the different topograaphies. Byusing the data interpreted from aerial photographs and visual interpretation, the data colllected from the study area was processed and analyzed by the special program naming SPANS. version 5.3 incorporated with OS/2 operating system. The method applied in the study is based on the overly analytical techniques which were employed to solve conditons as required. The 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers of the area was completely overlayed. The final outcome is an information map of relationships between forest types, and soil series upon diffeent topographies. It covers an areaa of the eergreen forest dry dipterocerp forest and lod clearing area of which are soil series for example, Ml, Li, outcrops along the foot hill and upon the mountat top . Whereas, the mixed deciduous foret teak pantation and agricultural area usuallyappeared on the pecific topography which contains soil series Ks, Tp etc in old levee Mi Li Bg etc soil series within dissected errosion surface including fans and thin layered sioilds mixed with rock outcrops on hilly and montainous area.
1. Introduction
The world population is now increasing while world natural resources are still limited. Thus, human basic needs, for ezxample, food, shelter, dress and medicinal suply, are highldemanded. Such high demand creates a conflict among land hungers.. In lessening nearly unsolvable confilicts, rational allocation of land use and utilizaation of land resources sshould be enhanced. This guideline leads to the GIS (Geographic Information System) employment.
2. Geographic Information System Technology
2.1 GIS techonology today is considred a very important tool in land use allocation because it can offer a mean of understanding utlization dealing with jproblems of the natural resources bumanbeing need. The conflicts between the limited resources and the bhuman ever increasing requirement cause forest deterioration and change the dense forest into raid urbanized area.
2.2 GIS helps people to organize the data for solving such problems and provides an efficient mean for analyzing and systhesizing different information and maps into a homogeneous usable product.
2.3 Now the GIS technology has been developed very fast. It is widely accepted as an esential tool for the efffective utilization of geographic information
3. Objectives.
A Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot in amphoe Ngao, Lampang, northern Thailand, is situated between the lalitudes 18 30 - 18 35 and the longitudes 99 50 - 99 55. It approximately covers 86 square kilometers.
The climate in the area is mainly influenced by north east and south w west monsoons, and also seasonal depressions. due to the regular blows of nonsoons all through the year, Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot has three different seasons the rainy the cool and the hot dry seasons. Rainfallll distribution and temperature affect greatly on the forest landcover and the soil series of different topographies of the area.
5. Source of Data
5.1 forest Type Map Scale 1:50, 000 OF 1983-1984. (Ground Truth Data had Already Been Observed and Checked in 1993)
5.2 Royal Thai survey department's Topograhic map, scale 1:50,000
5.3. Soil Series MAP SCALE 1:100,000
6. Procedure
6.1 Hardware and software employed.
Hardware
6.1.1. Everex model 486/33
6.1.2. Digitizer Table A1 size
6.1.3 Colour plotter A0 size
6.1.4. Tektronix colour inkjet printer
Software
The software Spans (Spatial Analysis System) package version 5.3 of Typac company, Canada, consists of 14 Modules, Its main modules are Tiding mokule, Spans Map module and Spans GIS module employed incorporation with OS/2 operating system.
6.2 Methodology
6.2.1 Data Input: Before digitizing by tydig moduls. subdirectory was created in the computer, then tyding module was employed to take the point (node), are (line) from a topographic map (river, road). After digitized session, the outcome is digitized map containing several points and nodes (vector data). Refigitizing once more for forest cover and soil series data were made to show forest land cover map and soil series map (soil series map is a soil series appeared upon the different typographies ) So the final outcome is the digitized map containing several polygons (vecter data). After finishing digitized session insert topological (attributes by open spread sheet in spans Map module and then translate the vector data and raster data to Quarter which has been analysed by overlying between forest covers and soil types.
6.2.2 Data Storage
With Spans GIS module, study area has been identified to fix it mapping position in accordance with the variety of spatial data of different scale and projection combined.
6.2.3. Data Manipulation and Analysis
Bring quadtree type of data of a Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot to analyse by overlaying method (soil series has been overlaid by forest landcover)) The analysis employs the overlay analytical technique which is imprerative for the Spans GIS module.
6.2.4 Output & Display
The area of 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers shows completely the relationship between forest type. man made activities and soil series appeared on different topographies.
7. Result
The area of 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers of Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot shows completely the relationship between forest land cover and soil series appeared upon different topographies. It covers an area of the evergreen forest, dry dipterocarp forest ad old clearing area of which are soil series for example, M1. Li, Bg and other types appeared upon topographically dissected eosin surface including fans, and thin layered soils mixed with rock outcrops along the foot hill and upon the mountain top. Whereas, the mixed deciduous forest. teak plantation and agricultural area usually appeared on the specific topography which contains soil series Ks Tp etc. in old levee Ml Li Bg etc soil series within dissected erosion surface including fans and thin layered soils mixed with rock outcrops on hilly and mountainous area.
8. Discussion
The GIS technology brings Samuel on computer based set of procedures to store a manipulated geographical; referenced data ad displays them in the common and understanding media, such as,. mapping papers, thales of attributes, aerial photographs and satellite imageries.
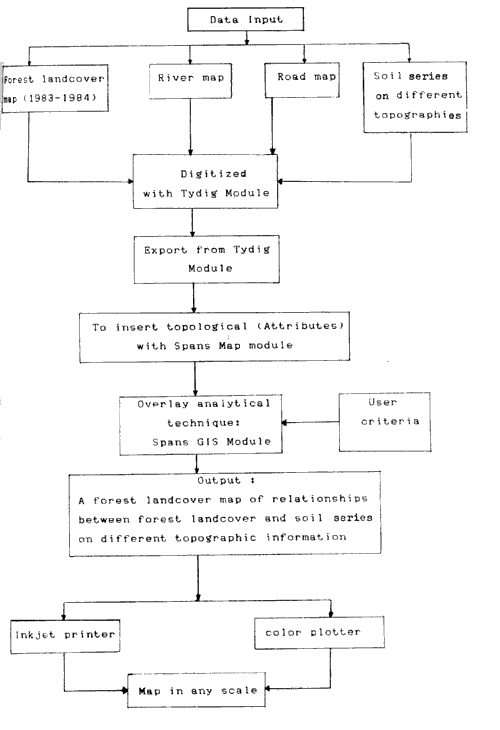
Chart Showing the Process of GIS on a Mae Huad Decmonstrative Forest Plot, Amphoe Ngao, Lampang Province
Table Showing Overly of Forest Land cover and Soil Series on Different Topographies of Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot
Remark
EF: Evergreen forest
MDF: Mixed deciduous forest
DDF : Dry dipterccarp forest
TP : Teak plantation
OC: Old clearing area
AA: Agricultural area
DESIF: Dissected erosion surface including fan topography
MAM: Hill and mountain topography
OL: Old levee topography
References
A compartive study on relatonships between forest types, man-made activities and soil series upon different topographies was conducted at a mae huad demonstrative forest plot, amphoe ngao of lampang province in northern thailand. The purpose of the study is to make a forest Landcover map of a Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest plot which relates to the soil ser4ies appeareeupon the different topograaphies. Byusing the data interpreted from aerial photographs and visual interpretation, the data colllected from the study area was processed and analyzed by the special program naming SPANS. version 5.3 incorporated with OS/2 operating system. The method applied in the study is based on the overly analytical techniques which were employed to solve conditons as required. The 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers of the area was completely overlayed. The final outcome is an information map of relationships between forest types, and soil series upon diffeent topographies. It covers an areaa of the eergreen forest dry dipterocerp forest and lod clearing area of which are soil series for example, Ml, Li, outcrops along the foot hill and upon the mountat top . Whereas, the mixed deciduous foret teak pantation and agricultural area usuallyappeared on the pecific topography which contains soil series Ks, Tp etc in old levee Mi Li Bg etc soil series within dissected errosion surface including fans and thin layered sioilds mixed with rock outcrops on hilly and montainous area.
1. Introduction
The world population is now increasing while world natural resources are still limited. Thus, human basic needs, for ezxample, food, shelter, dress and medicinal suply, are highldemanded. Such high demand creates a conflict among land hungers.. In lessening nearly unsolvable confilicts, rational allocation of land use and utilizaation of land resources sshould be enhanced. This guideline leads to the GIS (Geographic Information System) employment.
2. Geographic Information System Technology
2.1 GIS techonology today is considred a very important tool in land use allocation because it can offer a mean of understanding utlization dealing with jproblems of the natural resources bumanbeing need. The conflicts between the limited resources and the bhuman ever increasing requirement cause forest deterioration and change the dense forest into raid urbanized area.
2.2 GIS helps people to organize the data for solving such problems and provides an efficient mean for analyzing and systhesizing different information and maps into a homogeneous usable product.
2.3 Now the GIS technology has been developed very fast. It is widely accepted as an esential tool for the efffective utilization of geographic information
3. Objectives.
- To investigate by GIS techniques the relationaships between forest landcover and soil series upon different topographies.
- To produce a for3est landcover map of Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest plot in relation with the soil series appeared upon the different topographies.
- To search the functional feasibilities and efficiency of Everex 486/33 with Software SPANS (Spatial Analysis System package version 5.3 for process and overlay analytical technic\ques.
A Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot in amphoe Ngao, Lampang, northern Thailand, is situated between the lalitudes 18 30 - 18 35 and the longitudes 99 50 - 99 55. It approximately covers 86 square kilometers.
The climate in the area is mainly influenced by north east and south w west monsoons, and also seasonal depressions. due to the regular blows of nonsoons all through the year, Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot has three different seasons the rainy the cool and the hot dry seasons. Rainfallll distribution and temperature affect greatly on the forest landcover and the soil series of different topographies of the area.
5. Source of Data
5.1 forest Type Map Scale 1:50, 000 OF 1983-1984. (Ground Truth Data had Already Been Observed and Checked in 1993)
5.2 Royal Thai survey department's Topograhic map, scale 1:50,000
5.3. Soil Series MAP SCALE 1:100,000
6. Procedure
6.1 Hardware and software employed.
Hardware
6.1.1. Everex model 486/33
- CPU 80486, 32 bits capacity , speed 33 M Hz
- Hard disk (Internal) capacity 300 MB
- Geographic color monitor 124 x 768
6.1.2. Digitizer Table A1 size
6.1.3 Colour plotter A0 size
6.1.4. Tektronix colour inkjet printer
Software
The software Spans (Spatial Analysis System) package version 5.3 of Typac company, Canada, consists of 14 Modules, Its main modules are Tiding mokule, Spans Map module and Spans GIS module employed incorporation with OS/2 operating system.
6.2 Methodology
6.2.1 Data Input: Before digitizing by tydig moduls. subdirectory was created in the computer, then tyding module was employed to take the point (node), are (line) from a topographic map (river, road). After digitized session, the outcome is digitized map containing several points and nodes (vector data). Refigitizing once more for forest cover and soil series data were made to show forest land cover map and soil series map (soil series map is a soil series appeared upon the different typographies ) So the final outcome is the digitized map containing several polygons (vecter data). After finishing digitized session insert topological (attributes by open spread sheet in spans Map module and then translate the vector data and raster data to Quarter which has been analysed by overlying between forest covers and soil types.
6.2.2 Data Storage
With Spans GIS module, study area has been identified to fix it mapping position in accordance with the variety of spatial data of different scale and projection combined.
6.2.3. Data Manipulation and Analysis
Bring quadtree type of data of a Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot to analyse by overlaying method (soil series has been overlaid by forest landcover)) The analysis employs the overlay analytical technique which is imprerative for the Spans GIS module.
6.2.4 Output & Display
The area of 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers shows completely the relationship between forest type. man made activities and soil series appeared on different topographies.
7. Result
The area of 77.62 square kilometers out of 85.56 square kilometers of Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot shows completely the relationship between forest land cover and soil series appeared upon different topographies. It covers an area of the evergreen forest, dry dipterocarp forest ad old clearing area of which are soil series for example, M1. Li, Bg and other types appeared upon topographically dissected eosin surface including fans, and thin layered soils mixed with rock outcrops along the foot hill and upon the mountain top. Whereas, the mixed deciduous forest. teak plantation and agricultural area usually appeared on the specific topography which contains soil series Ks Tp etc. in old levee Ml Li Bg etc soil series within dissected erosion surface including fans and thin layered soils mixed with rock outcrops on hilly and mountainous area.
8. Discussion
The GIS technology brings Samuel on computer based set of procedures to store a manipulated geographical; referenced data ad displays them in the common and understanding media, such as,. mapping papers, thales of attributes, aerial photographs and satellite imageries.

Chart Showing the Process of GIS on a Mae Huad Decmonstrative Forest Plot, Amphoe Ngao, Lampang Province
Table Showing Overly of Forest Land cover and Soil Series on Different Topographies of Mae Huad Demonstrative Forest Plot
| Legend | Area (%) | Area (km2) |
| EF of DESIF | 1.49 | 1.16 |
| EF on HAM | 4.00 | 3.10 |
| MDF on OL | 0.14 | 0.11 |
| MDF on DESIF | 26.24 | 20.37 |
| MDF on HAM | 30.19 | 23.43 |
| DDF on DESIF | 0.62 | 0.48 |
| DDF on DESIF | 7.20 | 5.59 |
| TP on OL | 0.85 | 0.66 |
| TP on DESIF | 22.51 | 17.47 |
| TP on HAM | 2.28 | 1.77 |
| OC on DESIF | 0.90 | 0.70 |
| OC on OL | 2.27 | 1.76 |
| AA on OL | 0.15 | 0.11 |
| AA on DESIF | 0.57 | 0.44 |
| AA on HAM | 0.61 | 0.47 |
| Total of 15 classes | 100.00 | 77.62 |
Remark
EF: Evergreen forest
MDF: Mixed deciduous forest
DDF : Dry dipterccarp forest
TP : Teak plantation
OC: Old clearing area
AA: Agricultural area
DESIF: Dissected erosion surface including fan topography
MAM: Hill and mountain topography
OL: Old levee topography
References
- Burough, P.A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems for Land Resources Assessment. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1986 .193p.
- Kaew Nualchawce. "Geographic Information Systems. Paper presented at the international Seminar on Human Resources Requirements for Natural Resources Information Management. AIT Bangkok 27-27 Auguse 1952. 11p