| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1991 ---> Poster Session 2 |
Extraction and recognition of
map symbol from Topographical Map
Takashi
Hoshi
Institute of Information Science and Electronics
University of Tsukuba
Tennodai, Tsukubam Ibaraki, Japan
Toru Takaki
Master's Programs in Scientific Technology
University of Tsukuba
Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan
Institute of Information Science and Electronics
University of Tsukuba
Tennodai, Tsukubam Ibaraki, Japan
Toru Takaki
Master's Programs in Scientific Technology
University of Tsukuba
Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan
Abstract
Recently, combination of topographical map data and remote sensing image data is socially required. In this paper, extraction and recognition of map symbols from completed topographical map is described, in order to get more useful information by combination of topographical image with remote sensing image. But there are great many symbol images in topographical map. Some symbols overlap one another, so it is difficult to extract and recognition of map symbols. The method with hole feature for recognition of map symbols will be shown. Some symbols in a topographical map on a scale 1:25,000 are used as the research data.
1. Introduction
At present, maps are used in many fields. In highly information society, digitization of map information which called "computer mapping" has been required for more efficient utilization. Maps are almost printed matter, but maps have a vast amount of information. With computer mapping, it will be possible to use geographical information with other media. Some institution management systems such as electric light pole and wire, and water pipe, are based on the geographical information. Combination of topographical map data and remote sensing image data make it easy to analyze data, and it is socially required. To use geographical information, map information such as symbols, characters and some lines must be taken, and a database which includes map information's must be established. There are two methods to establish map database. The first is digital mapping with map data which extracted when map is drown up. The second is extraction and recognition of map information data from ready-made map is the second.
The purpose of this research is to extract and recognize map symbols from ready-made topographical map to get geographical map data. But there are great many symbol image in topographical map. Some symbols overlap one another, so it is difficult to extract and recognize map symbols. For overlapped image, using hole feature would be very useful.
In this paper, recognition of map symbols with hole feature is described. A topographical map on a scale of 1:25,000 is used as the research data. Figure 1 is an example of such map symbols.

Figure 1 Map symbolsin topographical map
2. Recognition of several map symbols
Before recognition of map symbols from topographical map, recognition elements for recognition of several components which consist of map symbol with original symbol is described in this paper.
2.1 A kind of map symbols in topographical map.
After the scheme of map is decided, and some symbols and characters are displayed on map. Map symbols which are included in map on a scale of 1:25,000 are classified as follows: 1) topography 2 ) traffic institution 3) buildings 4) other structures 5) use land 6) boundary line. There are two type of map symbols. one is a fixed type symbol which has almost similar form at any map, and another is non fixed type such as boundary lines and contour lines. The former, such as symbols of buildings is used for extraction and recognition in this research, such as symbols of buildings is used for extraction and recognition in this research, are recognized separately.
2.2. Recognition elements of map symbols
For recognition of map symbols, two feature extractions are indispensable. The first is the extraction of several image components in case one symbol has plural components. The first feature is obtained with following feature elements: a number of hole, occupied rate of image in its circumscribed rectangle, a ratio of length to height, a number of geometrical feature points ( ends, junctions and crossings ) a direction of end points, width of lines and a rate of diagonal connection. The second feature elements are a ratio of several image size, a direction of one image from another, inclusive relation and a rate of separation. A process of thinning is performed for feature extraction of geometrical feature points. After all, two type of symbol image are stored. One is thinned image which called is skeleton, and another is raw image.
2.3 Recognition of several map symbols
Experiment of recognition of several map symbols was done with 50 types fixed symbols. With recognition elements which are described at previous paragraph, map symbols were recognized. Notice that map symbols are inputed separately. All map symbols were recognized based on investigation of several components and separated relations in other research.
3. Recognition of map symbols from topographical map
There are problems When recognition of map symbols from topographical map is performed with recognition elements as Section 2. A map has a vast amount of map symbols, and some symbols overlap one another. So recognition of map symbols is very difficult. In order to solve this problem , recognition of map symbols with hole image will be described. Many images which includes hole image exist in topographical map. Some fixed symbols and other map factor such as numerals, characters and railroad symbols frequently appear on map. There is a example of images which include hole image. Among such image, fixed map symbols have some fixed hole image. And such images have a stability comparatively. This research take note of circular hole image for recognition of symbols, and recognize map symbols which include its image.
3.1 Hole
One image which is enclosed with a frame shown as Figure 2 is classified into S and S. S is a part of black and S is white ( background). And S is classified into Sb which touches frame and Sh. Sh is called "hole". It is possible to extract a part of hole by using method of labeling process.
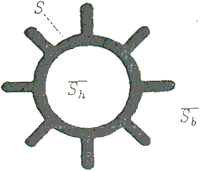
Figure 2 Hole
3.2 Research data
A topographical map "Northern Odawara" ( a scale of 1:25,000) is used as the original data. This map is 3 color-printed ( black, blue and brown) on background ( white ). The data of map is scanned by drum scanner. A resolution of 10 dots/mm is used in the experiment. The image data is taken with each color, and only black color image which draws fixed map symbols and any characters is used for extraction and recognition. A 512 X 512 pixel size is chosen as primary image for the experiment ( Figure 3).
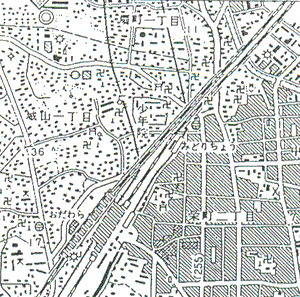
Figure 3 Research data
3.3 Procedure of recognition of map symbols
Symbols which include circular hole image is extracted in this experiment with taking note of form of hole image. Procedure of process is shown as follows:
Noise removal -
Isolated points are removed from the primary image.
Labeling -
On several image components, give a peculiar number by labeling process.
Hole extraction -
For labeled images, the existence of hole image is investigated. Only images which have hole images are extracted, and later a part of hole images are extracted.
Matching with circular image -
Hole images are matched with original circular image. Before matching, a scale of original image is transformed to a scale of hole images. Images which meet the matching condition is extracted. City hall
Recognition of map symbol -
Recognition of map symbols is done by matching with original map symbols. There are 13 symbols which include circular hole image ( Figure 4). Factory
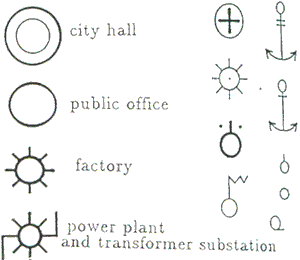
Figure 4 Map symbols including circular hole image
3.4 Experiment
The recognition of fixed map symbols which include hole image is performed with the procedure as former paragraph. Figure 3 is the primary image in this experiment. After noise removal, labeling and hole extraction, the image which includes hole image is shown as Figure 5, and Figure 6 is the hole image. Next, the matching with circular image is performed Smaller hole image produces mistakes of recognition by the error. The images that maximum length of its circumscribed rectangle is under 5 pixels are excluded from recognition. In the work done earlier, the object of extraction was the image which matched with a circumscribed rectangle as rate of 80%. But with that method, it takes long time for extraction of objective image, as there are great many other images then circular images in all hole images. So a process which extracts nearly circular image with a ratio of length to height of hole image is inserted in this research. Finally, the matching with the original symbols image is performed. The target symbols of recognition are "city hall", "factory", "power plant and transformer substation". The result of recognition of several symbols is shown as figure 7. The symbols in Figure 7 are transformed to the original symbols.
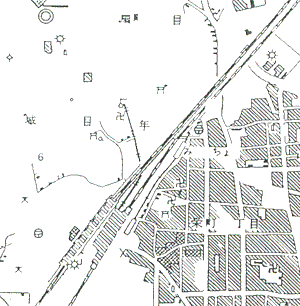
Figure 5 All image including hole
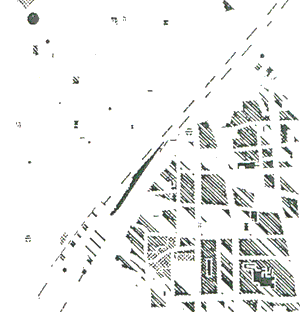
Figure 6 Hole images
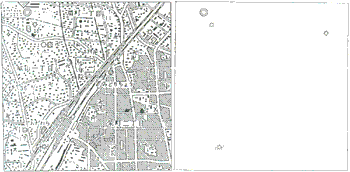
Figure 7 Result of the processing
4. Conclusion
In this paper, the method of extraction and recognition of a part of map symbol with hole feature was described. For recognition of fixed map symbols which include hole image, one symbol which overlapped another could be recognized. In particular, the symbol of "power plant and transformer substation" could be recognized in the experiment, though this symbol. overlaps with other line. For recognition with hole feature, restriction of recognition object would give high-speed processing. As smaller circular hole images have tendency to be classified as rectangular image, this research found out that it is necessary to perform extraction of geometrical feature points and so with thinning process. Other method by which the map symbols in which catting lines exist could be recognized and man-machine system will be researched for acquisition of map information at any time
Reference
- Hoshi, T. and Takaki, T., "Recognition of map symbol with geometrical feature", Proceedings of the 41st Annal Conference, Information Processing Society of Japan, 5M-8, pp212-213, 1990.9.
- Takaki, T. and Hoshi, T; "Recognition of map symbols form topographical maps with hole and geometrical feature", Proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on Functional Figure Information System ( Japan ) , pp19-24, 1991.4.