| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1991 ---> Poster Session 1 |
Application of Remote Sensing
data to epidemiological study
Saburo
Uchiyama
International Center for Medical Research,
Kobe University, School of Medicine, 7-5-1,
Kusunoki Chuo Kobe 650 Japan
Swee-Cheng Foo
National University of Singapore
10 Kent Ridge Crescent Singapore -0511
International Center for Medical Research,
Kobe University, School of Medicine, 7-5-1,
Kusunoki Chuo Kobe 650 Japan
Swee-Cheng Foo
National University of Singapore
10 Kent Ridge Crescent Singapore -0511
Abstract
In public health field, Remote Sensing has been tried in the study of disease-environment interrelation, particularly, the relationship between internal diseases, and land use in 8 areas in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan. A mathematical model was acquired by Uchiyama et al. This could be applied to other prefectures in Japan and would be useful in regional planning. Another study correlated Remote Sensing information with health consciousness among pupils in 4 cities and towns of the same prefecture. We found a significant correlation between the health index taken from a survey and Landsat data regarding land use.
Introduction
Since 1980, we have been conducting a study entitled "An epidemiological study on the Relation of Environment and Disease by Systematization of Remote Sensing data and Ground data" in Hyogo and Okinawa prefectures in Japan, Laguna area in the Philippines, and Singapore. We have started an epidemiological study on the relationship between Filariasis and human environment using Remote Sensing technology at the southern part of Thailand jointly with PSU. Results of the series of researchers achieved by our group have been reported at international and national conferences. Our ultimate object is to build mathematical models of human related factors, especially environmental factors, by using Remote Sensing data. We report seven results of our research works on Remote Sensing epidemiology.
Methods
Fig. 1 Shows the diagram of the analytical process.
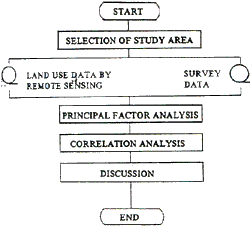
Fig. 1 Analysis Flow chart
Results
Research 1. Study on 8 pilot Area on Hyogo Prefecture
Hyogo Prefecture is known for its variety of regional characteristics in climate, topography, industry, mode of living, tradition and culture. This report shows the applicability of the tradition and culture. This report shows the applicability of the Remote Sensing method to the pubic health field and tries to build mathematical models between the disease and environment. From the Remote Sensing analysis, the eight pilot areas n Hyogo prefecture which has been selected in advance showed their characteristic land use of forest, agricultural land, town, city and water-covered areas. The Remote Sensing analysis was also coincided with the result of PCA (Principal Component Analysis). Furthermore, the selection of the pilot areas was shown to be possible with the Remote Sensing data by PCA only without using census data. It was shows that Remote Sensing data could almost compensate the cultural, social and economical data because high values of correlation coefficients in MRA (Multi regression analysis) were obtained. The number of people who died from hypertension and cardiovascular disease was estimated by the obtained multi-regression equation which had the highest correlation. coefficient with the areas of agricultural land, water - covered area and city as the variables. The estimated values by the MRA Method were little different from the census data. It was thought that the Remote Sensing technology was highly useful for investigations in the field of public health for prevention of diseases.
Research 2 . Study on 4 pilot areas in Hyogo prefecture
In research 1 where 8 pilot areas were studies, the areas were classified into 4 clusters. Research 2 was conducted to investigate the correlation between sense of health and recognition of environment between sense of health and recognition of environment among school children living in these 4 clusters and the Remote Sensing data. An investigation on health was carried out by questionnaires among 376 11- year old school children living in 2 cities and 2 towns in Hyogo Prefecture. Questions were related to the mind, body, daily habits, social life, awareness for own health, environment recognition and degree of satisfaction for the area they are living etc An analysis of relation between the state of health and living environment of children showed that there was a significant high correlation between health and increase ration of agricultural land, water and green. We obtained a conclusion that health index acquired from the health investigation which we prepared based on Cornell Medical Index has a significant correlation with natural environmental factors described by the Remote Sensing data.
Research 3. Study in Okinawa Prefecture
In this research, 33 cities and town in Okinawa where the natural environment and climate are closest to those in Southeast Asian Countries were selected. Since the applicability of Remote Sensing data to the field of public health has been proven, this study examined their relation with census data. Urban areas, forest, inhabited areas and agricultural land as defined in Remote Sensing data are compared with the habitable areas, forest, grasslands and cultivated areas as defined in the data prepared by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, and the Ministry of construction, Japan as census data. There was a correlation of r = .85 between inhabited area and habitable area, of r = .94 in forests, of r = .68 between forest and grasslands, of r = .80 between values. A land covering analysis by Remote Sensing data grasped nearly accurately actual land utilization, and it is clearly useful for area analysis.
Research 4. Study conducted at Laguna District in the Philippines.
This research was conducted mainly by Dr. Ruben N. Caragay and Ms. Ma Sarah Domingo of Comprehensive Community Health Program (CCHP) in the University of the Philippines. The questionnaire used Research 2. was utilized for the Filippino Children. A total of 356 samples were obtained. Based on the Landsat data and health survey data, an area environmental analysis and health problems were tackle. As was the case with the studies in Japan, we found a significant correlation between the two kinds of data.
Research 5. Awajishima in Hyogo Prefecture
Awajishima island which is located at southern part of Hyogo Prefecture consists of a city and 10 towns. The investigation included 278 items on physical conditions. The Remote Sensing data used a mesh unit of 1 km square irrespective of administrative division such as city and town.
Research 6. Remote Sensing Data analysis in Singapore.
In this study, we attempted to calculate pixels for land utilization classification for the area in the vicinity of the airport. The result was 1036 for urban fields, 1845, 1163 and 14 for ponds, 1100 for coastal water, 116 and 2520 for the sea, 1061 for clouds, 912 for barren land, and 880 for sandy area. The data used was photographed by Landsat on May 8, 1986. In analysis of Remote Sensing data for Singapore, it was impossible to specific the headquarters of people's life at one point in the country. This represents the difficulties in depicting disease and health map of the country broken down by regions. Remote Sensing data are quite useful for observing changes in environment and disease structure by time series analysis. We have demonstrated the applicability of Remote Sensing technology for following interrelation between environmental changes and disease structure by time series changes for 3,5 and 10 years.
Research 7. Epidemiological study on Filariasis in South Thailand.
Data from SPOT, a French satellite, was used in conducting the epidemiological study on filariasis in Narathiwat, South Thailand. Compared to Landsat, Spot data with high resolution was found to be effective indicators for visually and numerically determining the regional characteristics, topography, vegetation and land use of the area studies. Detailed on-site investigation is warranted.