| GISdevelopment.net ---> AARS ---> ACRS 1991 ---> Oceanography |
The Remote Sensing Grey Model
for Extracting the Informations on Marine Silts Suspended
Chen Xiao – xiang, Yi
Jian-chun and Li Tie-fang
Centre for Remote Sensing, Zhongshan Univ.
Guangzhou 510275, P,R. China
Centre for Remote Sensing, Zhongshan Univ.
Guangzhou 510275, P,R. China
Abstract
The grey feature of marine remote sensing information determines that extracting information’s on the suspended silts from it should use the method of grey mathematics and relative degree analysis.
Through the remote sensing test on marine silts suspended in Huangmao Sea, Yamen, Pearl River Mouth, the authors compared 3 kinds of suspended silts estimating models with relevant grey models, pointed out that grey model can obviously improve the estimating precision and, therefore, proved the marine grey theory introduled by prof. Li Tie-fang, i.e. the transmitting process of marine remote sensing information is a grey system with multi-variable.
The causes of using grey model being able to improve the precision of estimation of silt are as follows:
- The way of relative degree analysis is less affected by small sample.
- The processing of data adding up improved the linear future of data, so that it can match with actual changes of silt content.
- The values of different brightness are separately transformed by different ranges, so the total error will be decreased.
- The processing of data adding up may fully used known data, to some extent, the processing is equal to the processing of signal overlay, so as to enhance the signal/ noice rate.
Up to now, the remote sensing models in actual use on suspended silts are mostly the semi-experienced model combined physical model with statistics. According to water bodies in different marine areas, some models were introduced by some experts. the common models in use are as follows:
- To regard the spectral reflection of suspended silts as a linear
function.
S- A + B * R (l) -------------------------(1)
- To suppose that the vertical distribution of suspended silts is
equal in research area, and absorption coefficient, forward and backward
scattering coefficients are constant in given hours.

- To suppose that spectral scattering of silts in water is mainly Mie
scattering.
R = A + B ( 1 - eDS) ------------------- ( 3)
- To regard the transference of scattering signal of suspended silts
in air and in water as an exponential attenuation function, so logarithm
retrieval function is adopted.
Ln (S) = A + B * R ------------------------ (4)
- Proportional value model
S = A + B (Ri (l) / Rj(l) } ------------------------(5)
Note Here, S: Silts Content
R: Remote Sensing Data
i, j,: Different Bands i, j.
A,B,C,D: the coefficients to be determined.
- Statistical theory is based on the basis of large sample, but the sample is very difficult to collect when the satellite passes synchronously over sea. In a broad sea-area, even though several or teens sampling points could not be thought to be enough for it. In such case, the mathematical models built with statistics are of bad steady, and large fluctuations are often seen as the sampling points increase or decrease by one or two, hence larger error would be bring about with using such models in the estimation of silt content.
- Marine Remote Sensing Information is a synthetically reflection of marine optical information, in which, apart from the information on suspended silts, there are also other random information’s on air water boundary etc. when to set up mathematical model with correlation analysis, these interfering information’s without some processing will make impact on the model precision.
Prof. Li Tie – fang, Zhongzhan University, china, on the basis of the results of marine remote sensing research over several years, has developed a Marine Grey Theory, i.e. the transmitting process of marine remote sensing information is a grey system with multiple variables, including known information and some unknown information’s , being situated between1 the white system with all information known and the black system with all information unknown. According to Li’s theory and the feature of Marine suspended silts, we suggest the information extracting wag for the suspended silts as follows:
(a) Arrangement of data:
To arrange the data of samples according to the amount of silt content.
Y(k): the array for actual silts content.
Xj(k): the array for Remote Sensing Data.
Here,
J means the number of band.
K means array number of sample.
(b) Pre – processing of data
It needs that Remote Sensing Data are transformed by some of following suitable functions.
Average Transform

Logarithmic Transform:
Exponential Transform:
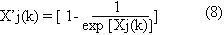
Proportional Value Transform:

(c) Data producing:
Array X’ j (k) and Y (k) are needed to be added up to get a new array X’ jn(k) and Yn(k).

(d) Relative function and relative degree
Supposing that there are two arrays G(k) and L(k) we define the relative function of the arrays G(k) and L(k) as follows:
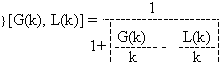
and define the relative degree of the arrays G(k) and L(k) as follows:
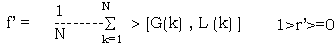
So, the larger the value of r’, the closer the approach degree of two arrays and the better the application effect of relevant model.
(E) The evaluation of relative transformation coefficient U(k) Supposing that the array Yn(k) of silt content ad the array X’ jn (k) of remote sensing are correlated as follows:
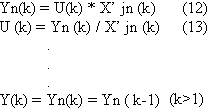
(G) To calculate extrapolation ally content of suspended silts from remote sensing data. After raw remote sensing data re transformed from transform (a) to transform (c), relevant (U(k) may by determined according to the range where the transformed remote sensing data lies in, and then the value of silts content Y many be estimated by using formulas (12) and (14).
III. The test compared Grey models with others.
The test, which was made at Huangmao Sea, Yamen, Pearl River Mouth in July 1988 as the satellite pass through, is to measure suspended silts content on the sea synchronal. The results and its calculation model are in table 1. In addition, the results of the estimation and check of other 4 synchronous sampling points are in table 21.
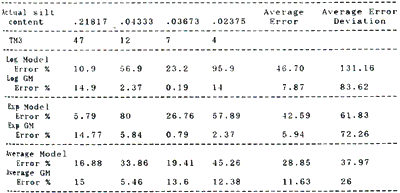
It can be found out from the table 1 and 2 that the error of estimated value of silts content with Grey model are significantly less than that with formulas 1, 3 and 4, and the range of the errs-variation obviously decreased . All of this means that the confidence of the prediction and extrapolation has improved. Multi-factor considered, average grey model adopted on this sea area has average error in 11.63% and average error-deviation in 26.62%.
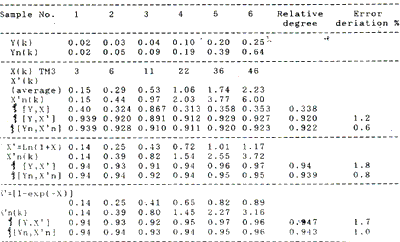
Table 2 The errors in actual and estimated values of silts content for TM3
The causes with which grey model can improve the precision of estimated silts content are as follows. (1) The relative degree analysis is less affected by small sample, in the case of small sample correlation coefficient may be seriously influenced by some sample , so the steady of the model may be bad as shown in table 3.

In the process of proportional value TM3/TM2, correlation coefficient is 0.123 and when first sampling point is cancelled it will become to 0.758 with the change of 84% as against the change of relative degree analysis being only 3%. The means that contributions of every sampling point towards relative degree is relatively even, and therefore, relative degree analysis is more effective and reliable in the case of small sample.
(3) The processing of data adding up make producing data array chang into an array with the feature of exact increase, improving the linear feature of data and making it match with actual changes of silt content.
(4) The processing of data adding up makes known data be fully used and to some extent is equal to the processing of signal overlay, so it is useful for improvement of signnoice rate and precision.
Conclusion
- The grey feature of marine remote sensing information determines that the extracting the information should use the methods of grey mathematics and relate degree analysis.
- Three kinds of suspended silt estimating models and relevant grey model have been compared and the results shows that grey model can make the estimating precision obviously improved, and the marine greytheorg founded by proof Li Tie fang i.e. the transmitting pr9ocess of marine remote sensing information is a grey system with multivariable, has been proved.
- In different sea area, different grey model should be adopted according to the feature of the ses area
- If the way of Grey model is used to the other filed of marine remote sensing, it will improve the precision of estimation.